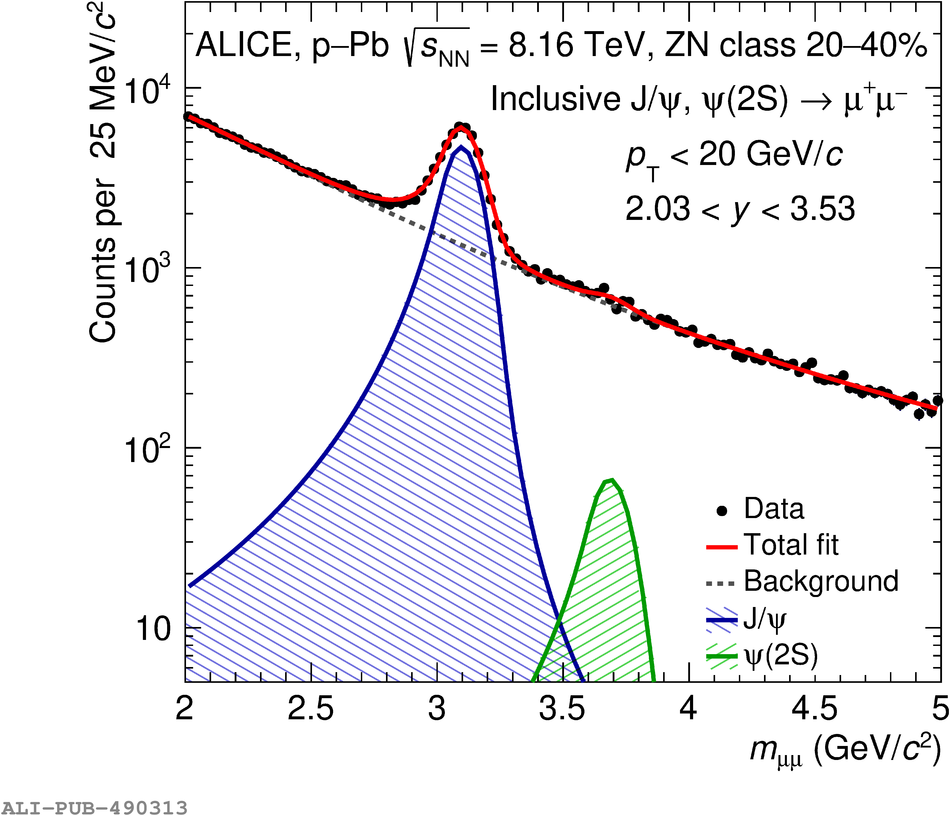
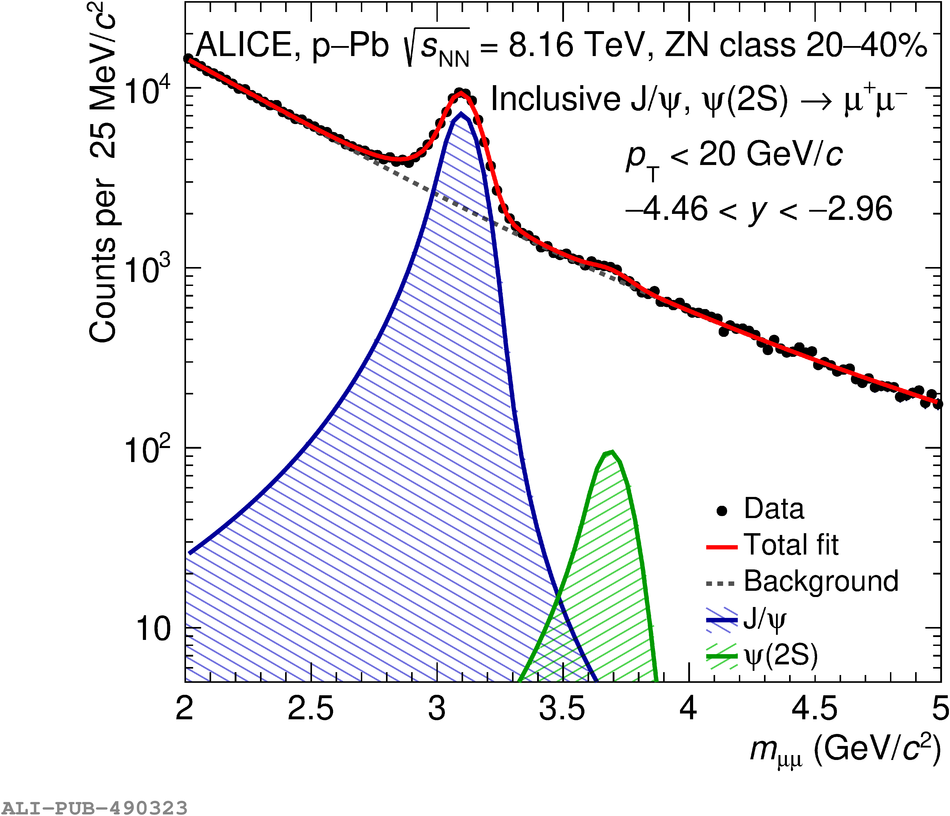
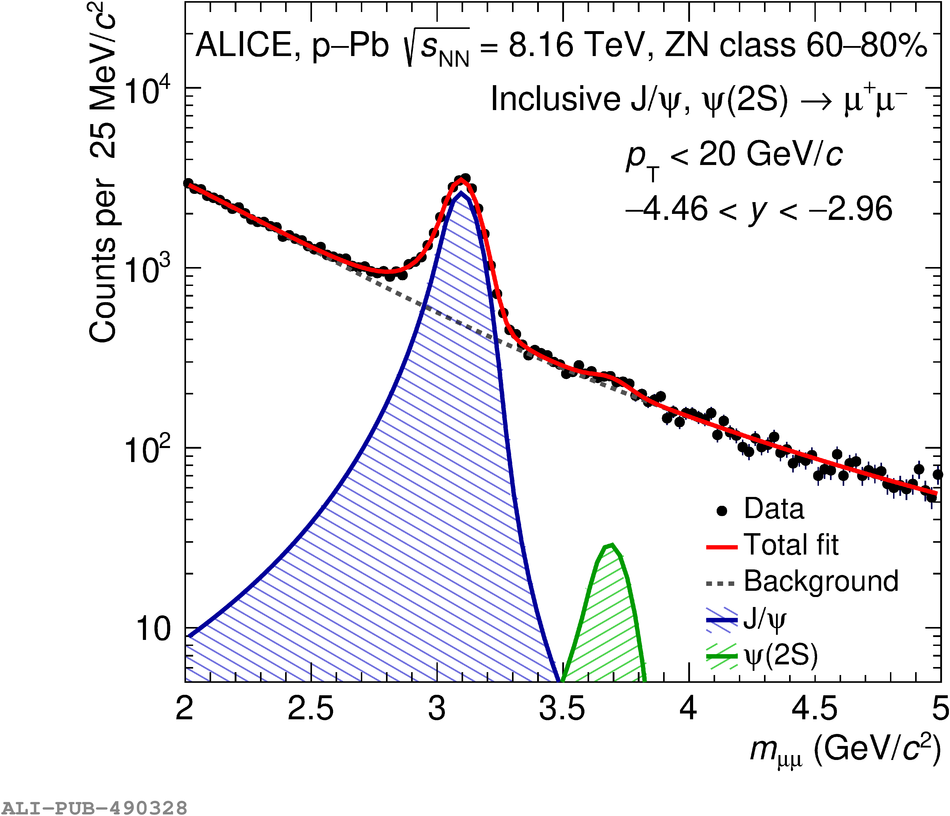
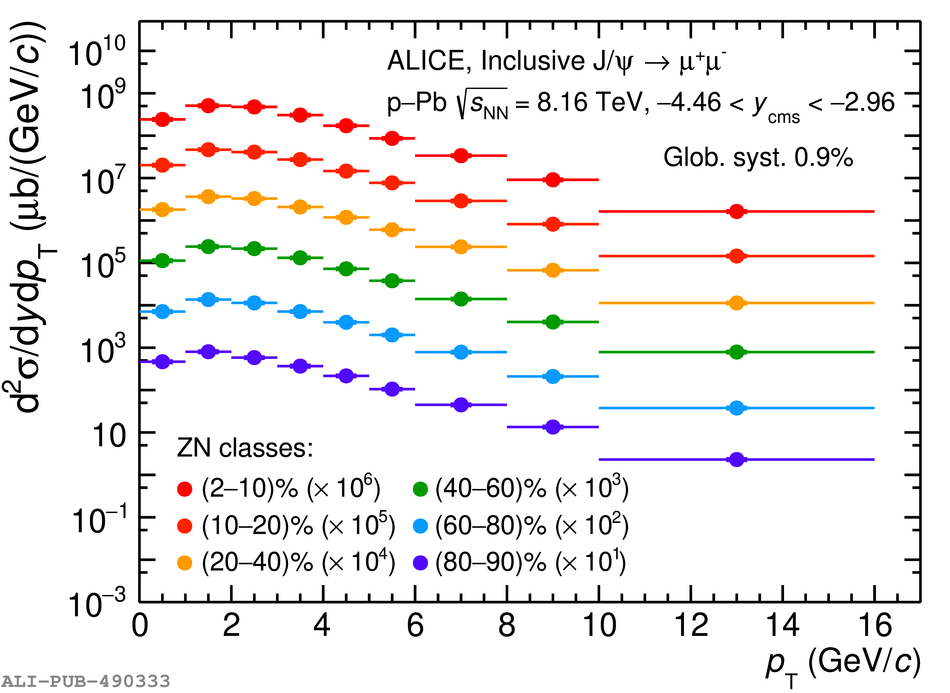
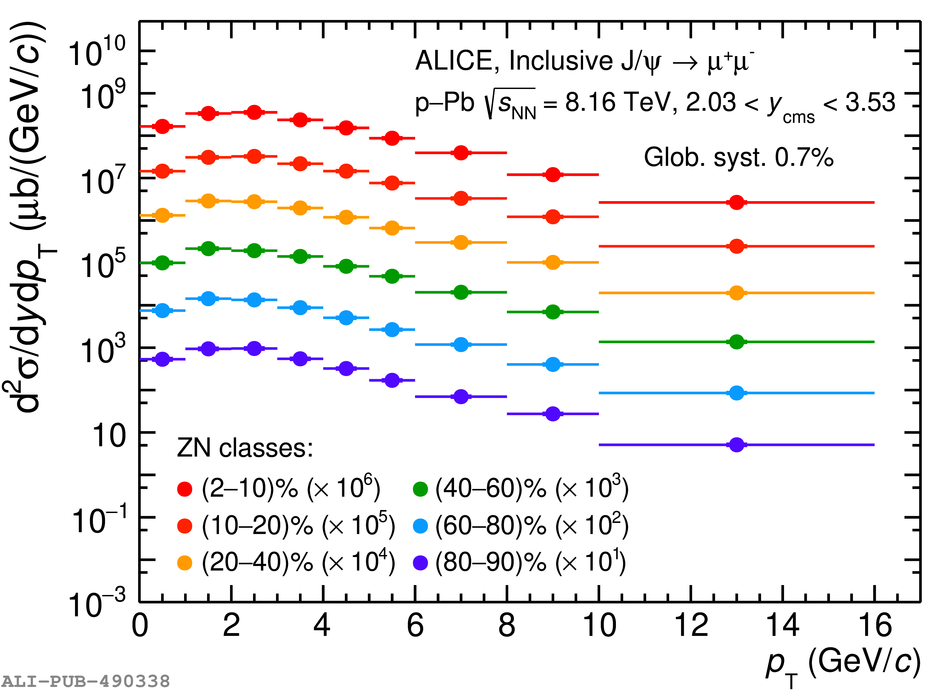
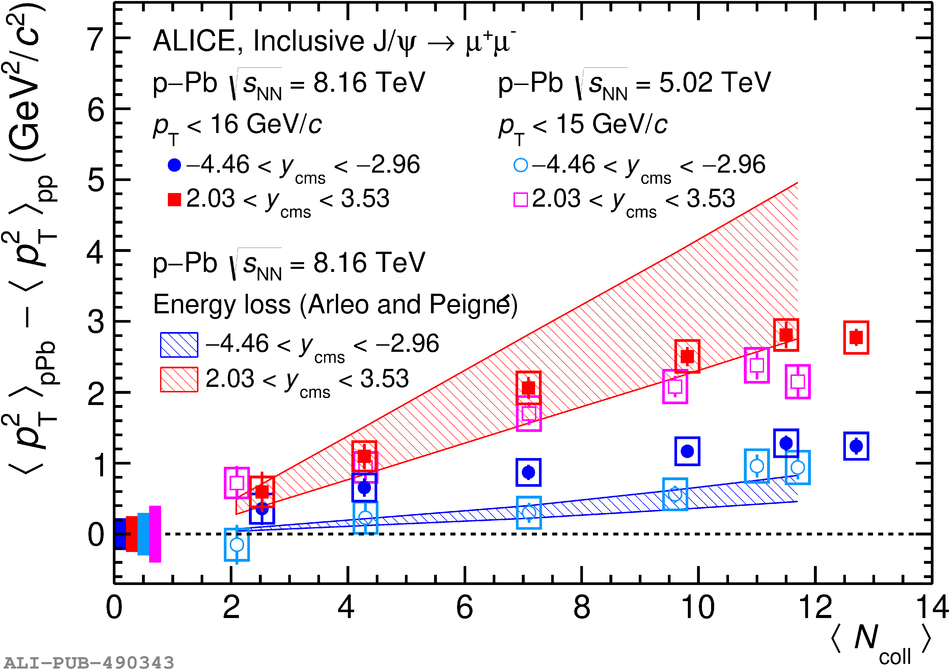
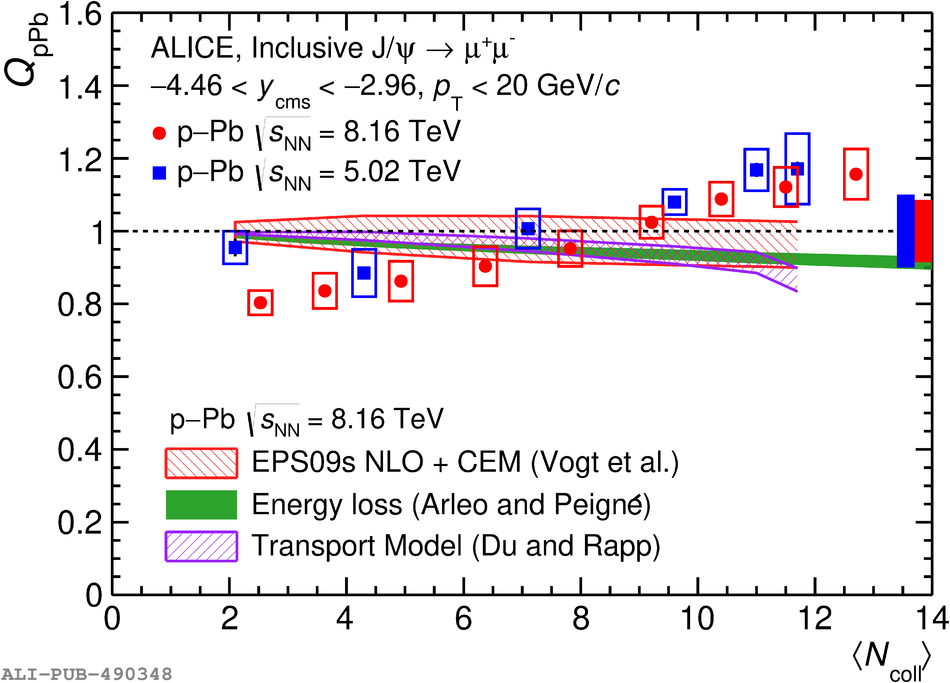
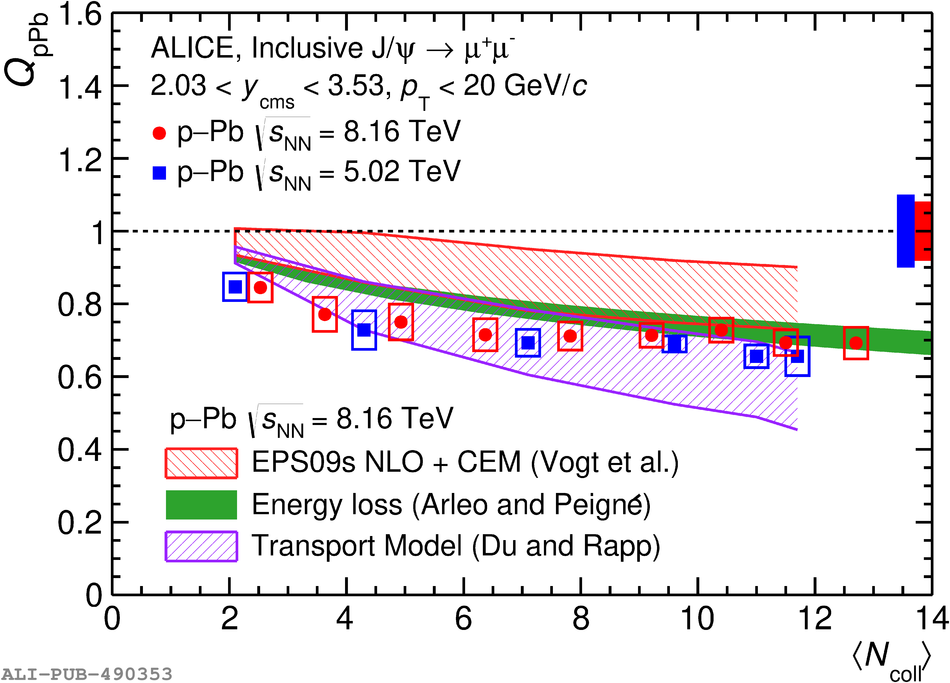
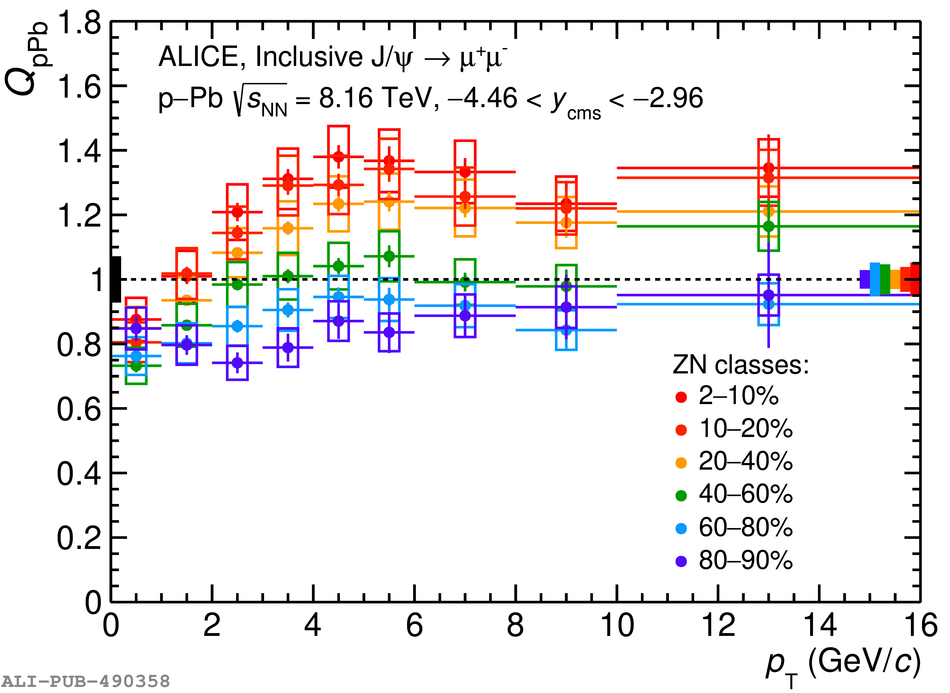
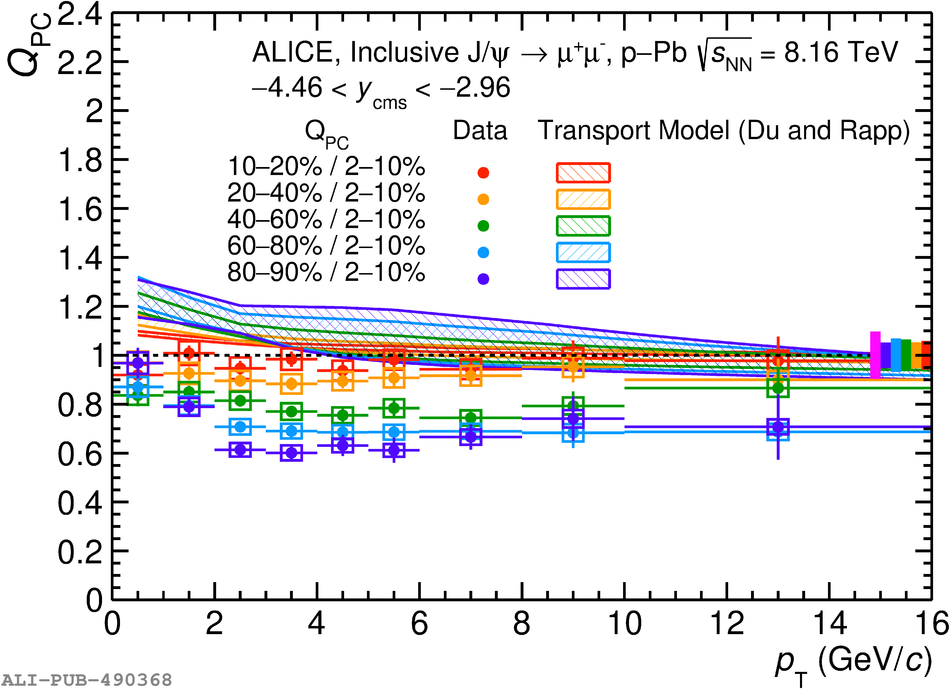
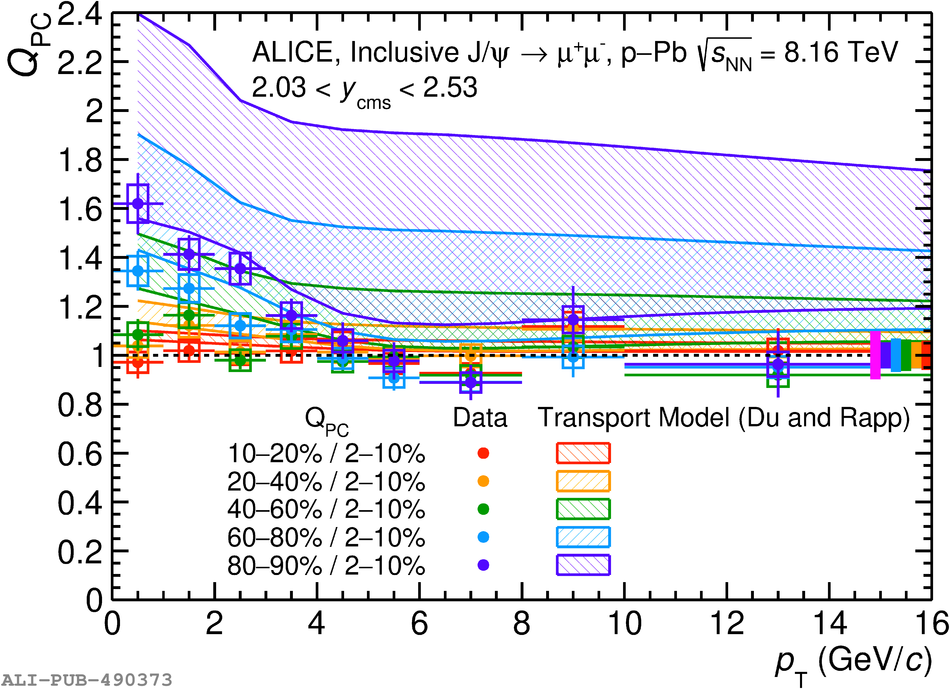
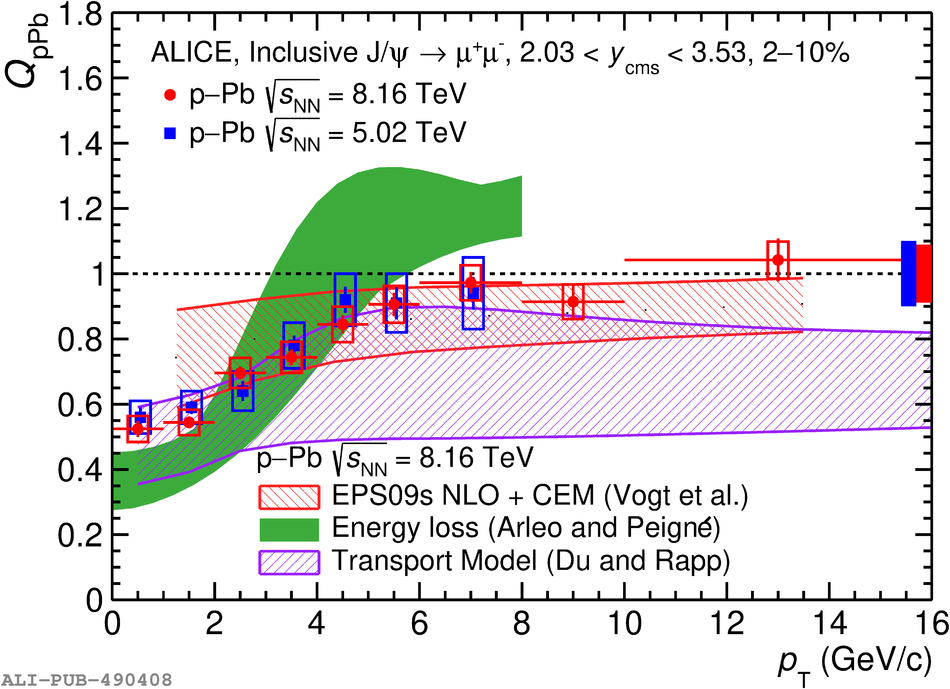
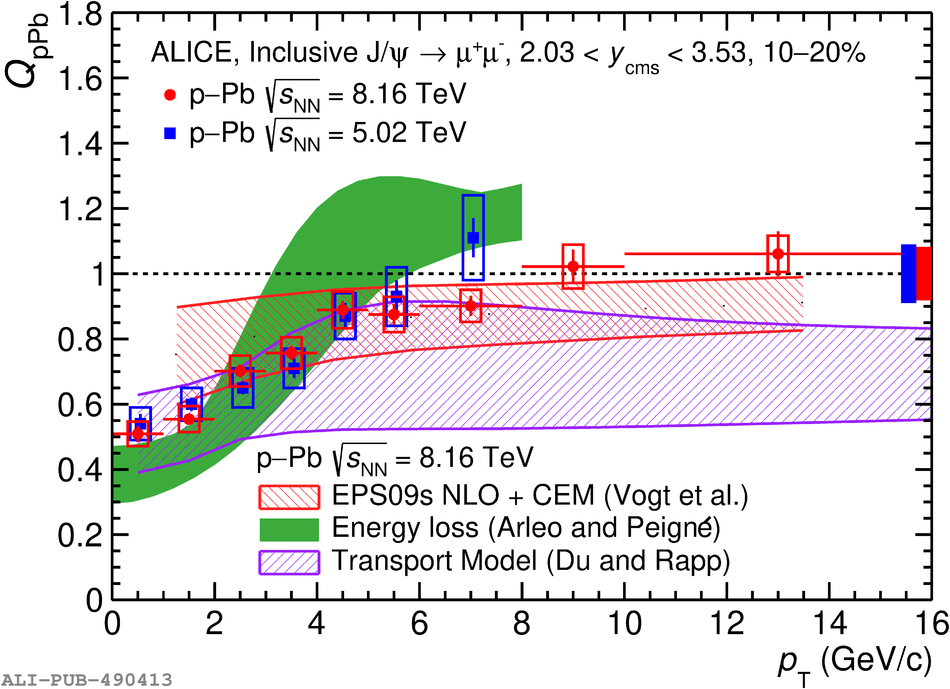
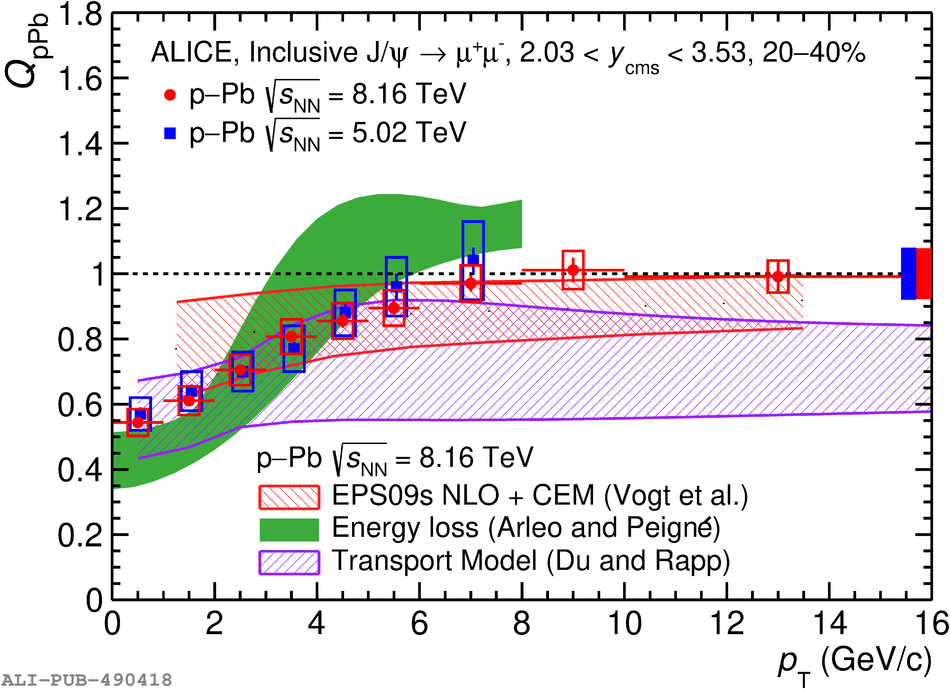
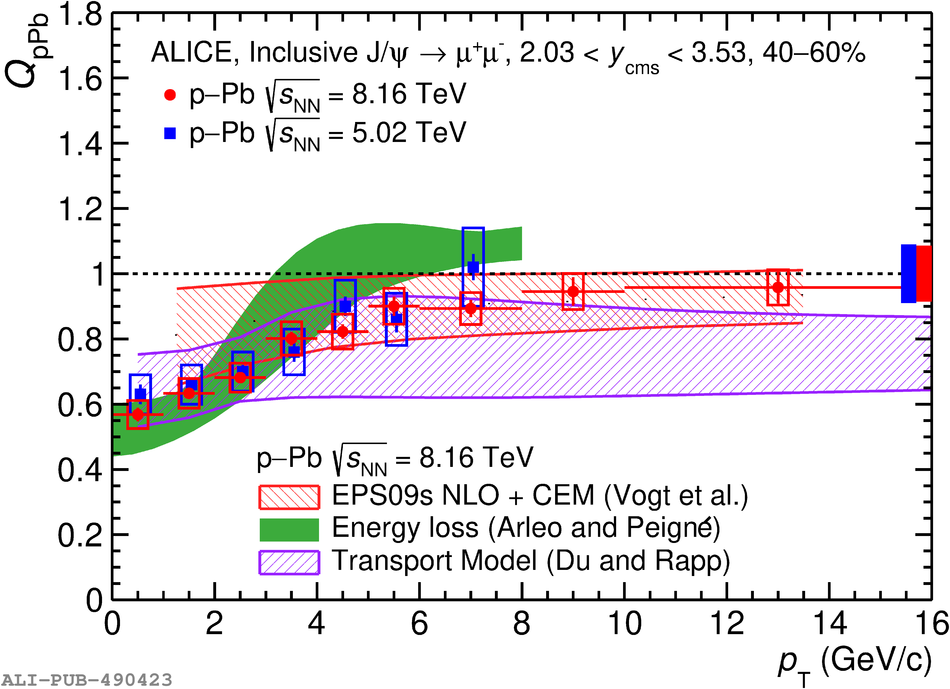
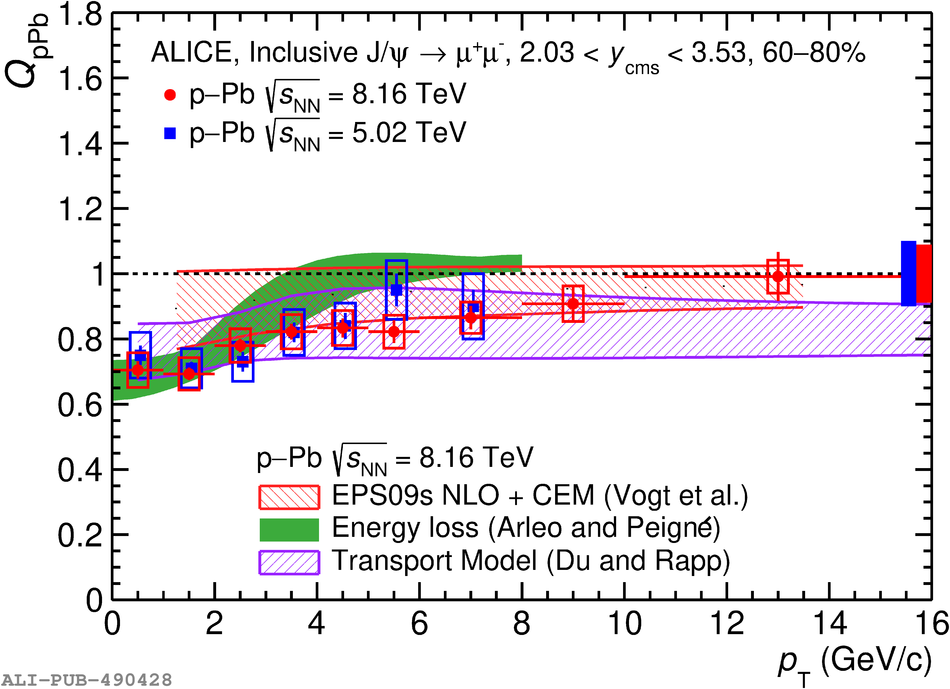
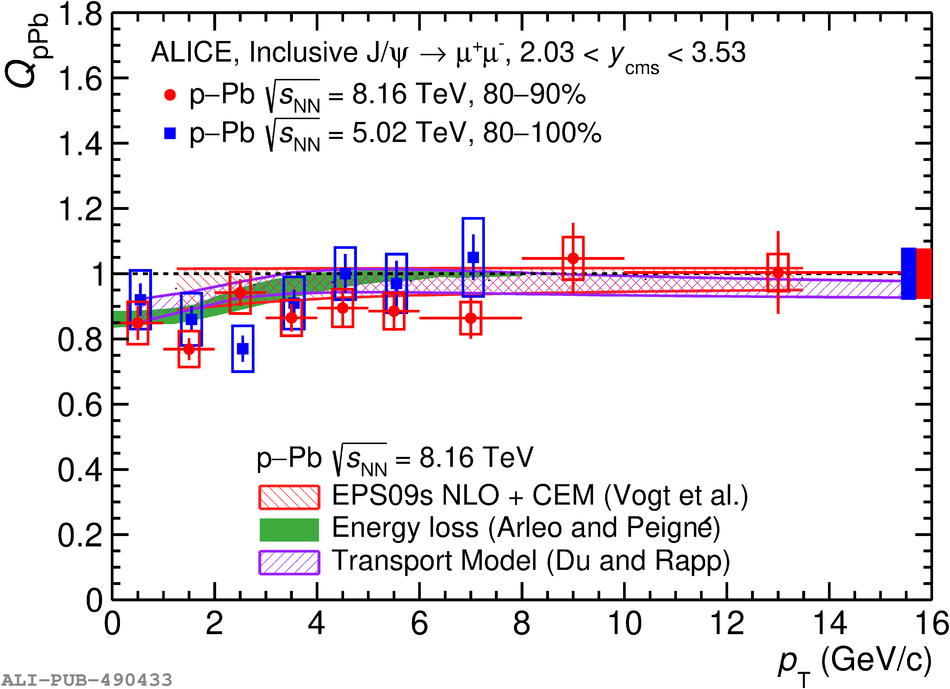
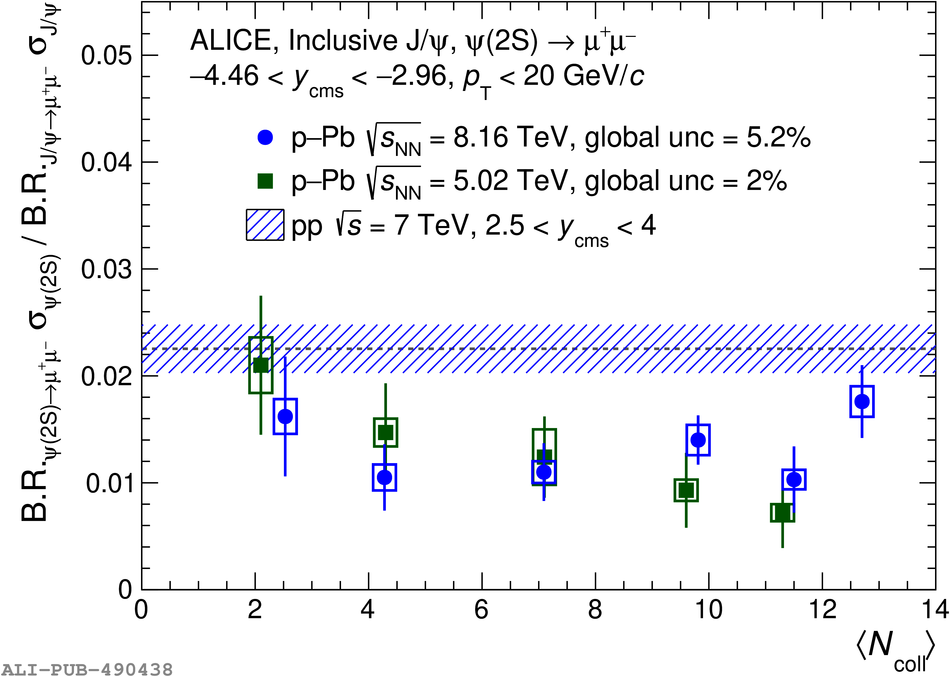
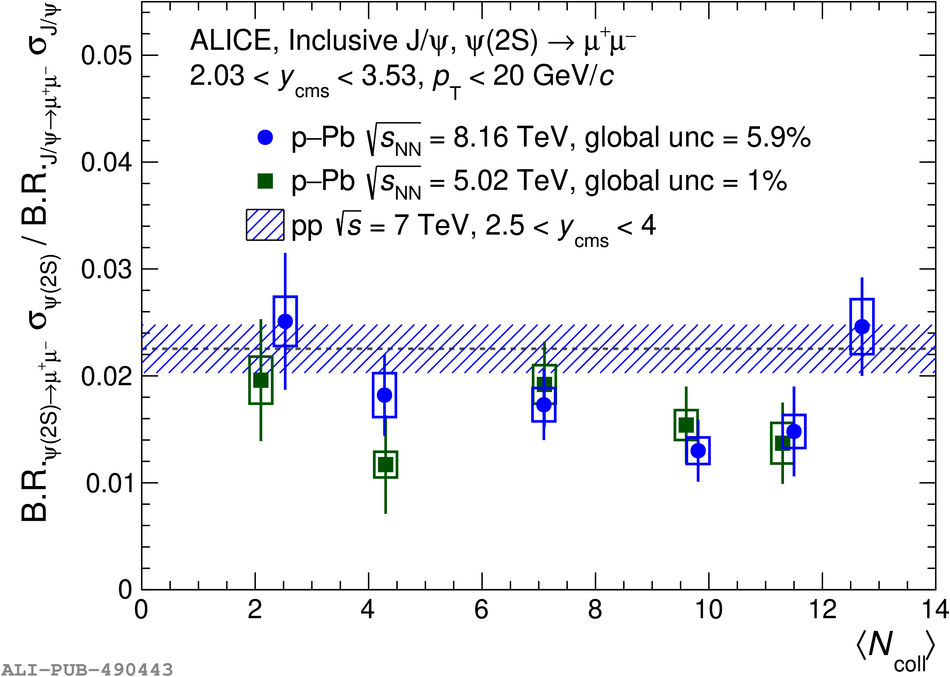
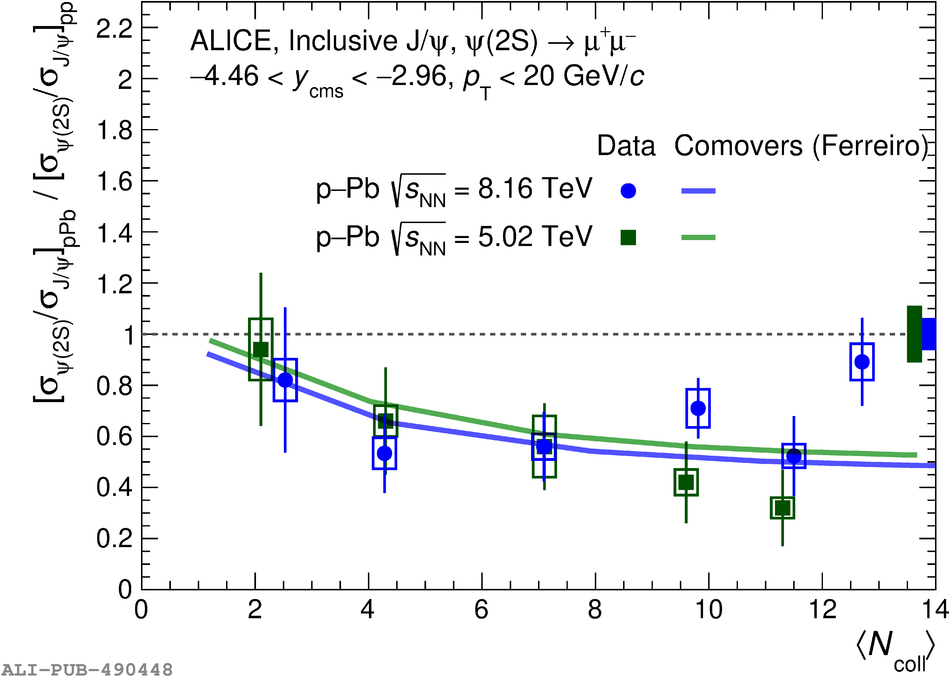
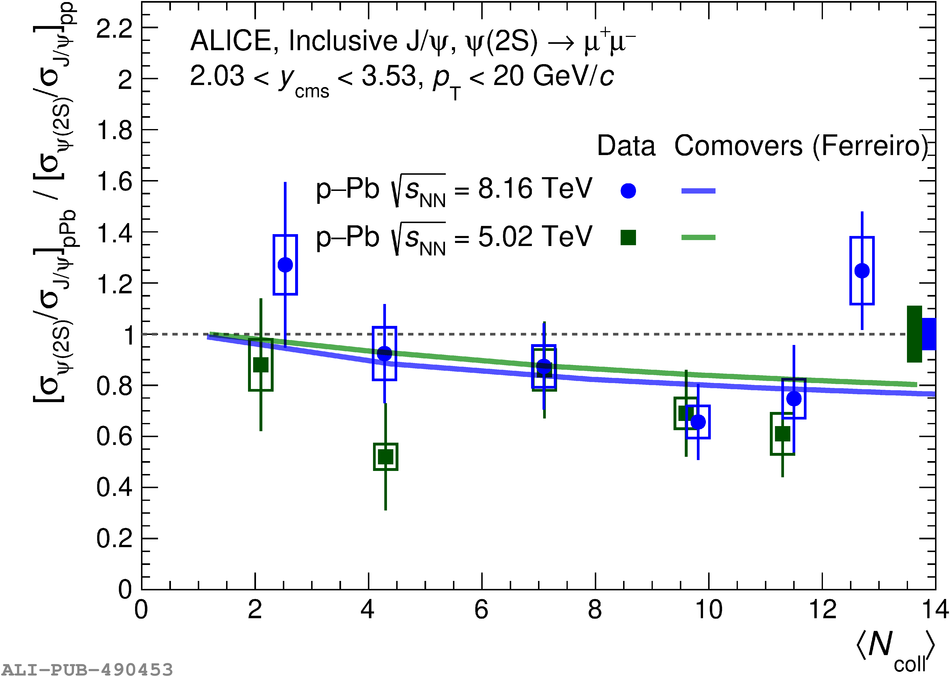
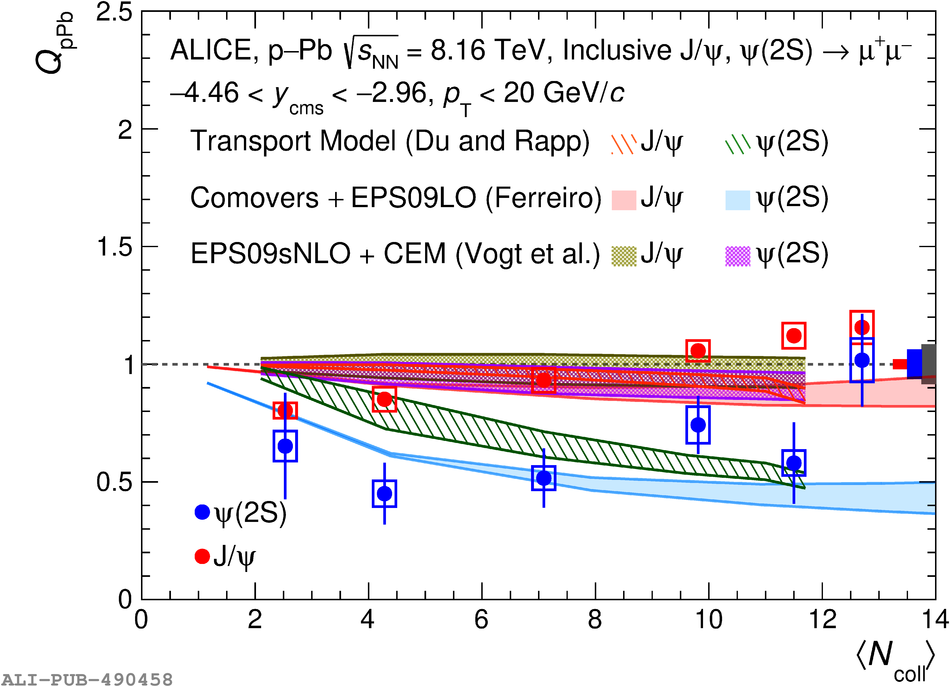
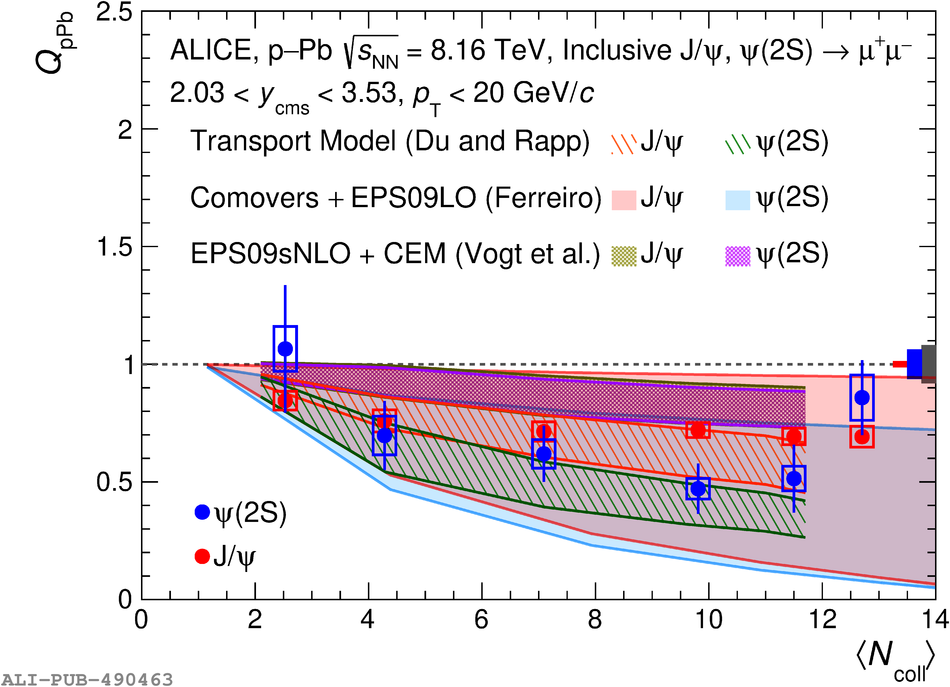
The inclusive production of the J/$\psi$ and $\psi$(2S) charmonium states is studied as a function of centrality in p-Pb collisions at a centre-of-mass energy per nucleon pair $\sqrt{s_{\rm NN}} = 8.16$ TeV at the LHC. The measurement is performed in the dimuon decay channel with the ALICE apparatus in the centre-of-mass rapidity intervals $-4.46 <~ y_{\rm cms} <~ -2.96$ (Pb-going direction) and $2.03 <~ y_{\rm cms} <~ 3.53$ (p-going direction), down to zero transverse momentum ($p_{\rm T}$). The J/$\psi$ and $\psi$(2S) production cross sections are evaluated as a function of the collision centrality, estimated through the energy deposited in the zero degree calorimeter located in the Pb-going direction. The $p_{\rm T}$-differential J/$\psi$ production cross section is measured at backward and forward rapidity for several centrality classes, together with the corresponding average $\langle p_{\rm T} \rangle$ and $\langle p^{2}_{\rm T} \rangle$ values. The nuclear effects affecting the production of both charmonium states are studied using the nuclear modification factor. In the p-going direction, a suppression of the production of both charmonium states is observed, which seems to increase from peripheral to central collisions. In the Pb-going direction, however, the centrality dependence is different for the two states: the nuclear modification factor of the J/$\psi$ increases from below unity in peripheral collisions to above unity in central collisions, while for the $\psi$(2S) it stays below or consistent with unity for all centralities with no significant centrality dependence. The results are compared with measurements in p-Pb collisions at $\sqrt{s_{\rm NN}} = 5.02$ TeV and no significant dependence on the energy of the collision is observed. Finally, the results are compared with theoretical models implementing various nuclear matter effects.
JHEP 02 (2021) 002
HEP Data
e-Print: arXiv:2008.04806 | PDF | inSPIRE
CERN-EP-2020-133
Figure group